THE OVARIES AND OVULATION
The ovaries
The ovaries are the female gonads, which contain egg cells (oocytes).
Ovulation
When the ovaries are stimulated by endocrinological
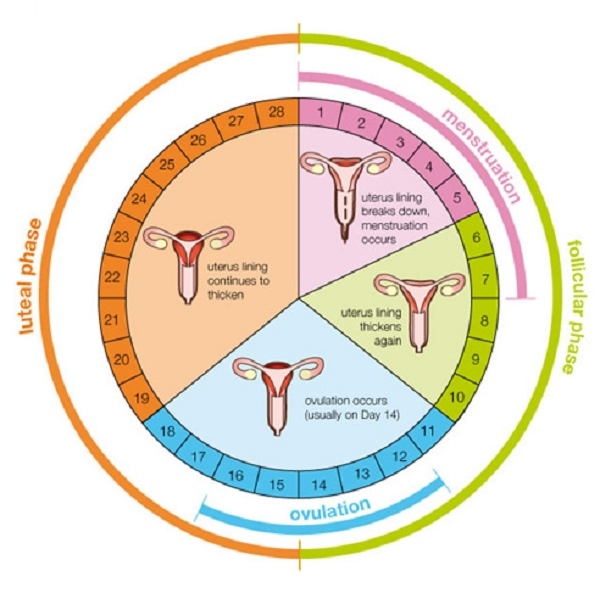
and neuronal factors, they respond by initiating the growth and development of several egg cells (oocytes). On average 1 to 2 of these oocytes mature and are released (ovulated) by the ovaries every 28 days (the average length of the menstrual cycle).
If an ovulated egg cell comes into contact with a sperm cell in the Fallopian tube, the process of fertilization takes place, whereby the two cells fuse. The implantation of the resulting embryo in the thick lining of the uterus leads to a pregnancy.The absence of embryo implantation, however, leads to shedding of the thick uterine lining, a process known as menstruation.
Hormones control menstruation and ovulation, which are the 1st and 3rd phases of the menstrual cycle, respectively. Hormonal imbalance, resulting in the absence of ovulation, can be due to disturbances in the function of the hypothalamus, the pituitary, the thyroid gland or the adrenal glands. Common causes include Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, obesity, occupational hazards, alcoholism and other intoxications. Premature Ovarian Failure also results in anovulation (the absence of ovulation).









